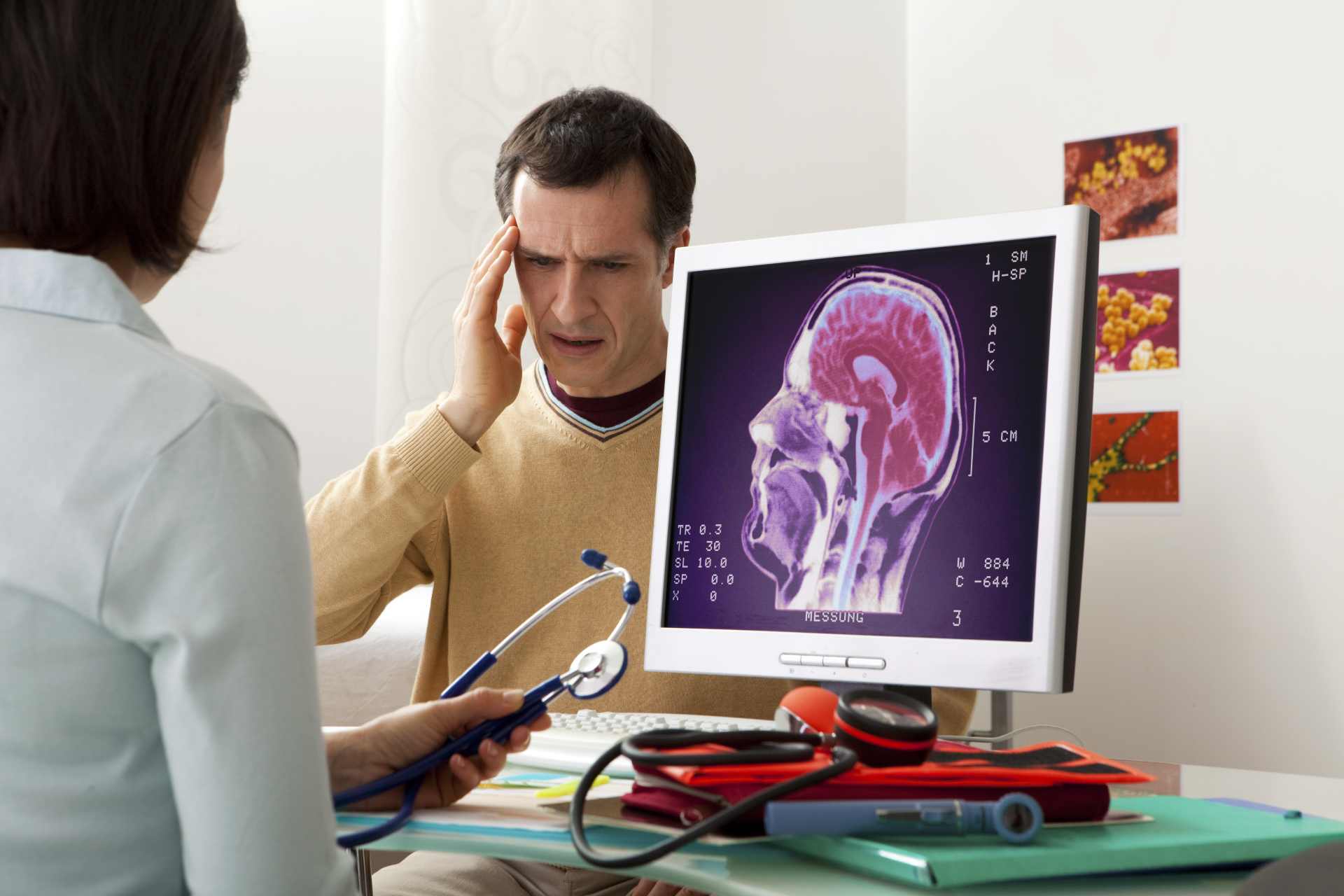
Brain bleeds are serious and potentially life-threatening injuries that can occur after a car accident. These injuries involve bleeding within the skull, which can increase pressure on the brain and lead to significant neurological damage or even death. Understanding the different types of brain bleeds, recognizing the symptoms, and knowing the importance of timely medical intervention are essential for anyone involved in a car accident.
What is a Brain Bleed? Types and Causes
A brain bleed, or intracranial hemorrhage, occurs when an artery in the brain bursts, causing localized bleeding in the surrounding tissues. This can lead to cell death and increase intracranial pressure, potentially damaging brain structures.
There are several types of brain bleeds, each with its unique characteristics:
- Subdural Hematoma: This type of bleed occurs between the dura mater (the outer membrane of the brain) and the brain itself. It often results from a severe head injury, such as those sustained in car accidents. Subdural hematomas can develop slowly or rapidly, depending on the extent of the injury.
- Epidural Hematoma: This bleed occurs between the dura mater and the skull. It is often caused by a traumatic blow to the head that fractures the skull, leading to arterial bleeding. Epidural hematomas can quickly become life-threatening if not treated promptly.
- Intracerebral Hemorrhage: This type of bleed happens within the brain tissue itself. It can be caused by trauma, such as a car accident, or other factors like high blood pressure or aneurysms. Intracerebral hemorrhages can cause significant brain damage due to the direct pressure on brain cells.
Car accidents are a common cause of these types of brain bleeds. The sudden impact can lead to a jolt or blow to the head, causing blood vessels to tear and bleed.
Symptoms of a Brain Bleed: When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Recognizing the symptoms of a brain bleed is crucial for seeking timely medical intervention. Symptoms can vary depending on the severity and location of the bleed but commonly include:
- Severe headache: Often described as the worst headache ever experienced.
- Nausea and vomiting: These symptoms can indicate increased intracranial pressure.
- Weakness or numbness: Particularly on one side of the body.
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech: This can be a sign of damage to the language centers of the brain.
- Loss of balance or coordination: Indicating possible damage to the cerebellum or other areas controlling movement.
- Changes in vision: Such as double vision or loss of vision.
- Confusion or altered mental state: Including memory problems and difficulty concentrating.
- Seizures: These can occur if the bleed affects the brain’s electrical activity.
If you or someone else exhibits these symptoms after a car accident, seek medical attention immediately. Delaying treatment can lead to worsening of the condition and potentially irreversible brain damage.
Diagnosis and Immediate Treatment of Brain Bleeds
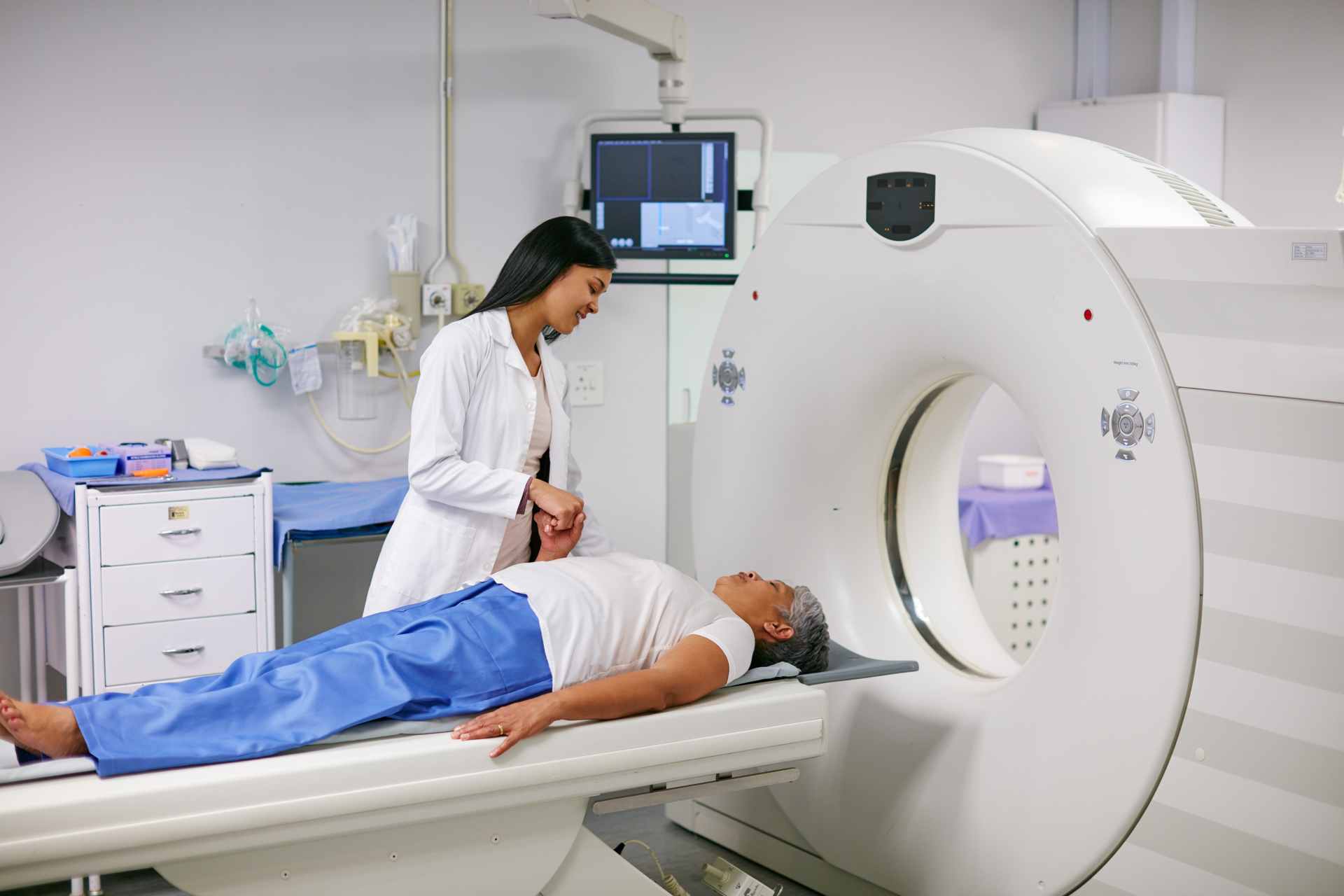 Diagnosing a brain bleed requires prompt and accurate medical imaging. The most common diagnostic tools include:
Diagnosing a brain bleed requires prompt and accurate medical imaging. The most common diagnostic tools include:
- CT Scan: A CT scan is often the first imaging test performed. It can quickly identify the presence, location, and extent of bleeding.
- MRI: An MRI provides more detailed images of brain tissue and is useful for identifying smaller or more subtle bleeds.
- Once a brain bleed is diagnosed, immediate treatment is essential to minimize damage and improve outcomes. Treatment options vary based on the type and severity of the bleed:
- Medication: Drugs may be administered to reduce swelling and control blood pressure, which can help limit further bleeding.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgical intervention is necessary to relieve pressure on the brain and remove accumulated blood. Procedures such as craniotomy or burr hole drainage may be performed.
- Monitoring and supportive care: Patients may require close monitoring in an intensive care unit (ICU) to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
Potential Risks of Untreated Brain Bleed
If a brain bleed goes untreated, the consequences can be dire. Untreated brain bleeds can lead to:
- Increased Pressure on the Brain: Accumulated blood increases intracranial pressure, which can cause severe headaches, vomiting, and even loss of consciousness.
- Permanent Brain Damage: Prolonged bleeding can result in irreversible damage to brain tissue, affecting cognitive and physical functions.
- Coma and Death: Severe brain bleeds can lead to a coma and, in some cases, death if not promptly addressed.
Early intervention is key to improving the prognosis for individuals with brain bleeds. Prompt medical treatment can reduce the risk of severe complications and enhance the chances of recovery.
Long-Term Effects of Brain Bleed and Recovery Process
The long-term effects of a brain bleed can vary widely, depending on the severity and location of the injury. Potential cognitive and physical impairments include:
- Memory loss
- Difficulty with speech or language
- Motor skill deficits
- Emotional and behavioral changes
The recovery process involves a combination of medical treatments and rehabilitative therapies such as physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy. Recovery can be a lengthy process, often requiring ongoing support and care.
Get Specialized Treatment for Car Accident Brain Injuries at AICA Orthopedics
For brain injuries sustained in car accidents, consulting specialists like neurologists is crucial. At AICA Orthopedics, we offer comprehensive care through a multidisciplinary approach. Our team includes neurologists, orthopedics, physical therapists, and more, all working together to create personalized recovery and rehabilitative plans. With 14 facilities across metro Atlanta, accessing expert neurological care is convenient and efficient.
For the best holistic care tailored to your needs, contact AICA Orthopedics today. Find the nearest AICA clinic near you to schedule an appointment and start your recovery journey.