Causes of Traumatic Brain Injuries
The brain is a complex organ, and trauma can have a wide range of effects depending on the type and severity of the injury. TBI occurs when a sudden impact or jolt disrupts normal brain function. TBIs are commonly caused by falls, car accidents, sports injuries, and violent assaults. The force of these incidents can cause the brain to collide with the inside of the skull, leading to bruising, bleeding, or tearing of brain tissue.
The most common types of TBI include:
- Concussion: A mild form of TBI often caused by a direct blow to the head.
- Contusion: A bruise or bleeding on the brain, typically from a severe blow.
- Diffuse Axonal Injury: One of the most severe types of TBI, where the brain’s connective nerve fibers are sheared by sudden deceleration.
- Penetrating Injuries: When an object pierces the skull, damaging brain tissue.
- Second Impact Syndrome: When a second TBI occurs before the first has healed, leading to rapid and often fatal brain swelling.
Risk factors for TBIs include participating in high-impact sports, failing to wear protective headgear, or experiencing violent accidents. Additionally, those with a previous brain injury are more susceptible to further damage.
Diagnosing Traumatic Brain Injury
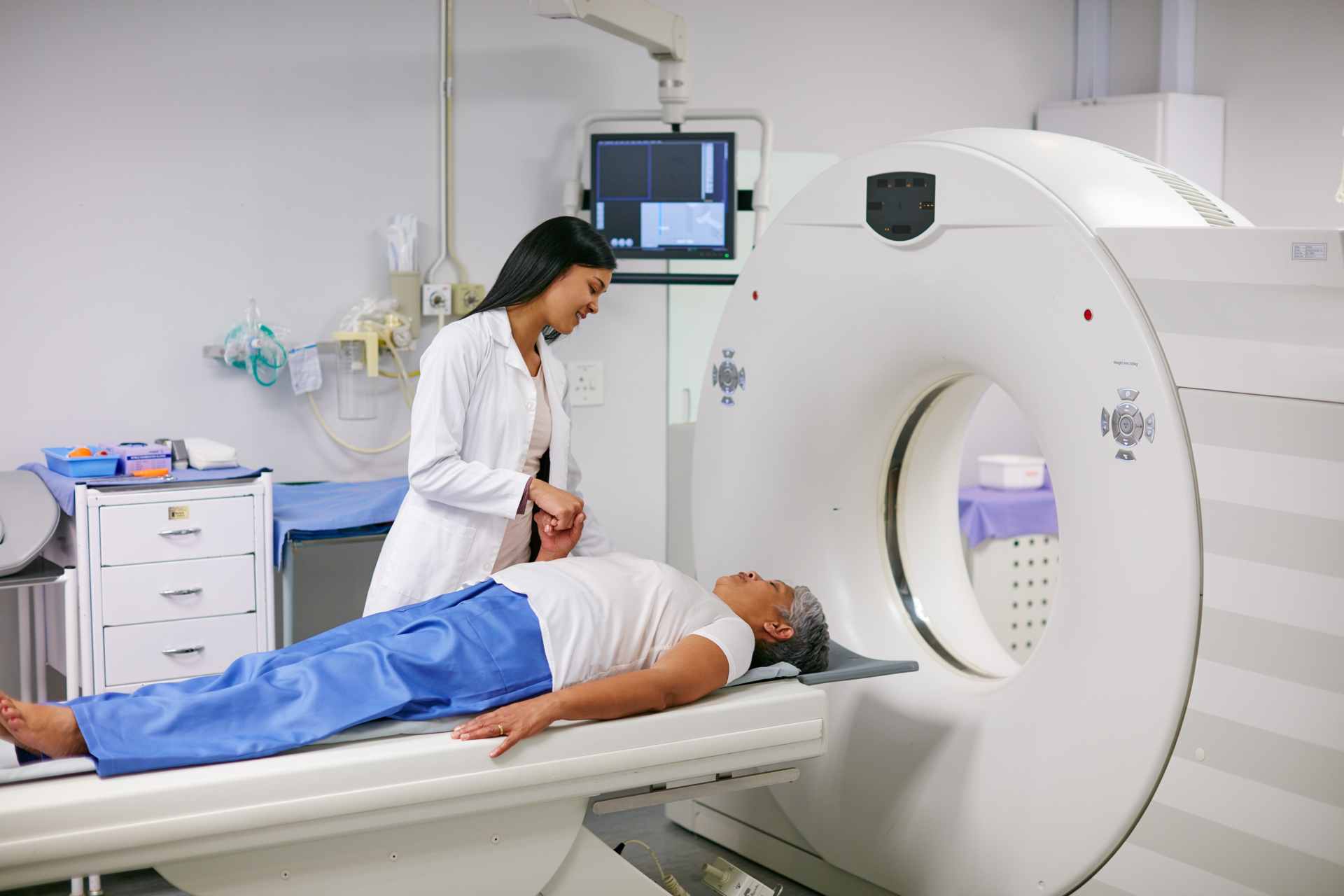
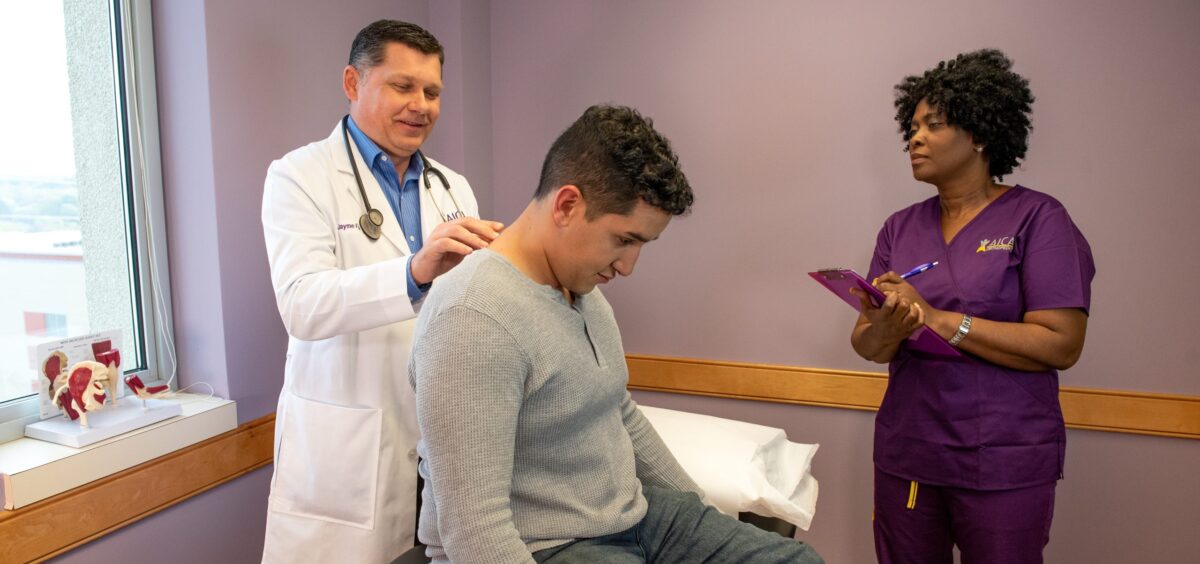
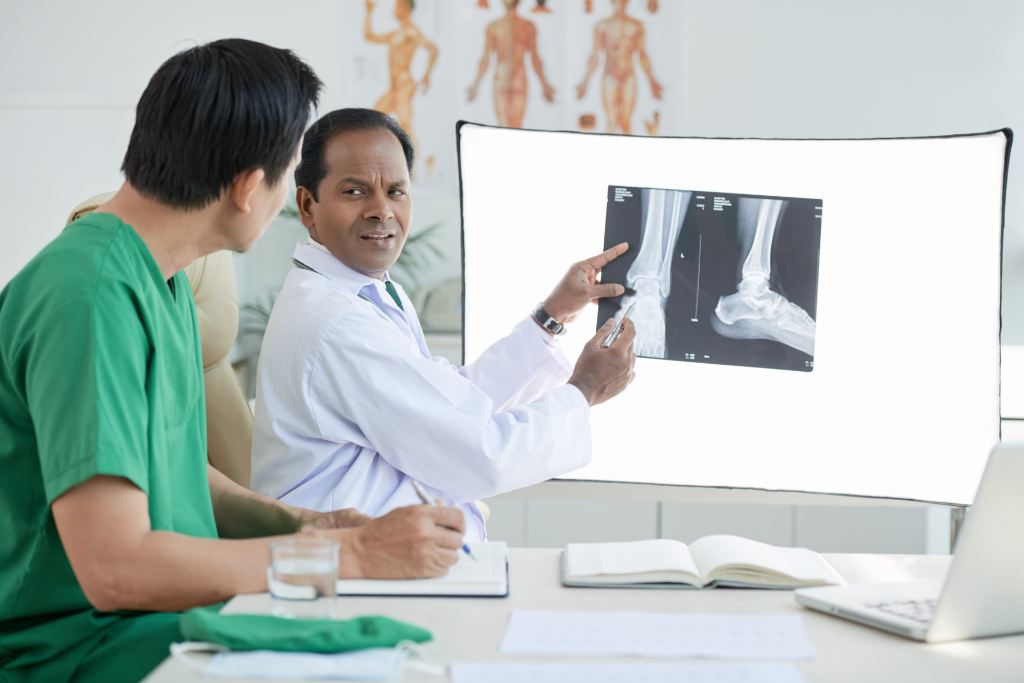
Diagnosing a traumatic brain injury as soon as possible is essential for successful treatment. At AICA Orthopedics, we use the latest medical imaging technology to provide an accurate diagnosis. CT scans and MRIs are commonly used to detect internal bleeding, bruising, or swelling in the brain. Our specialists will also conduct a series of neurological tests to assess your cognitive function, memory, and reflexes.
Our doctors may ask about the events leading to the injury, as well as your symptoms, including headaches, dizziness, nausea, confusion, or vision problems. Accurate information helps us determine the extent of the injury and plan for the most effective treatment. With a clear diagnosis, we can create a comprehensive recovery plan to address both immediate and long-term health concerns.